Hanging Wall Moves Upward Shallow
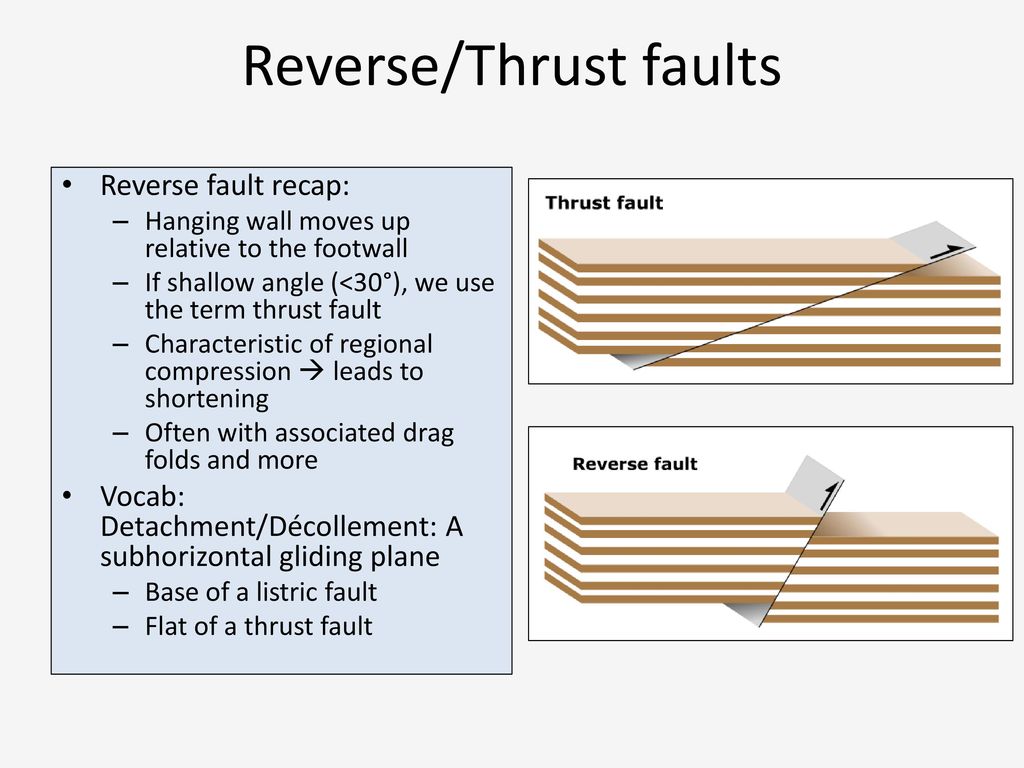
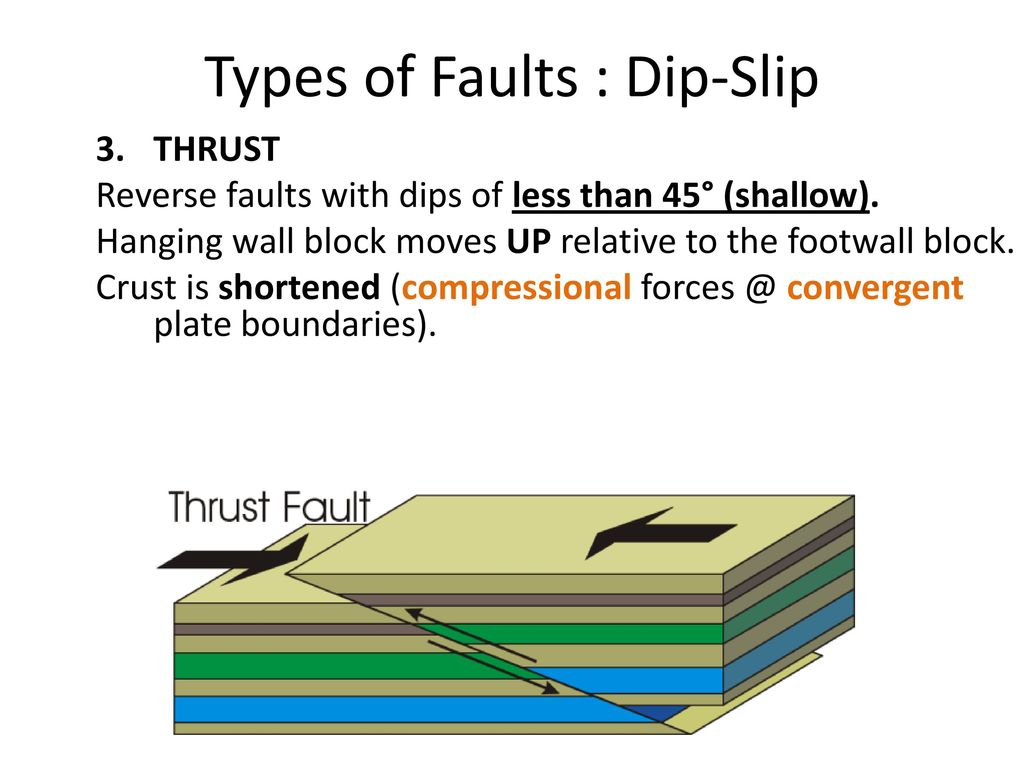
Thrust faults with a very low angle of dip and a very large total displacement are called overthrusts or detachments.
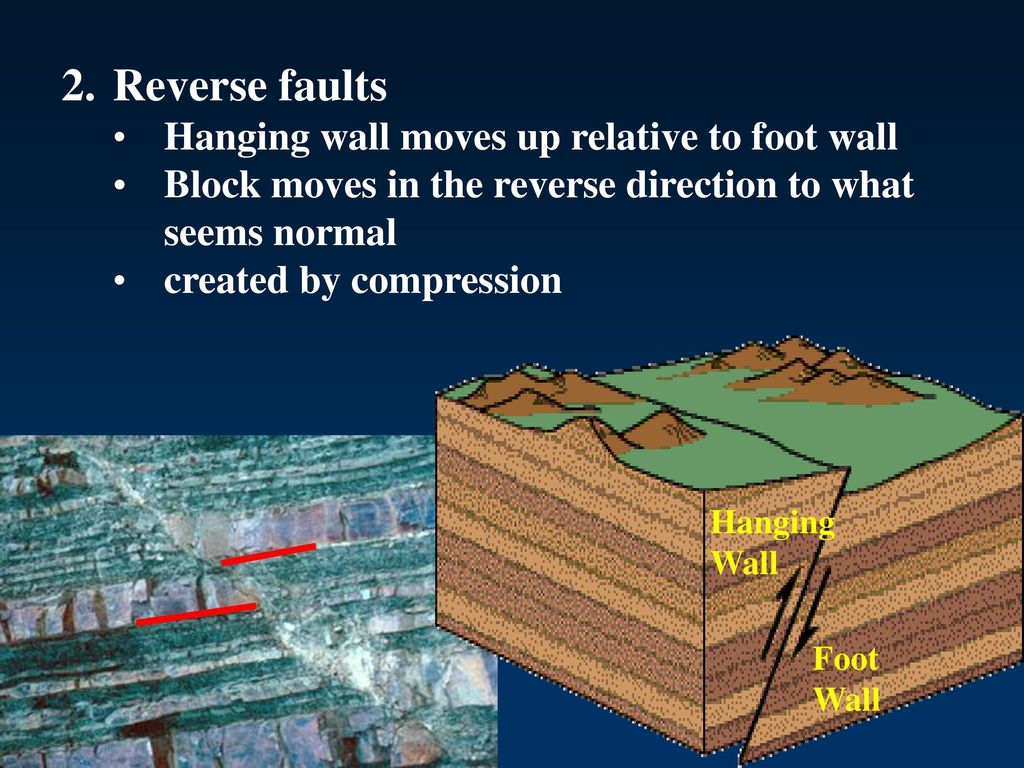
Hanging wall moves upward shallow. Hanging wall lies to the left of the footwall d. Footwall lies vertically above the hanging wall c. Reverse shear stress at sufficient depth within a fault plane can induce ductile shear forming a fine grained metamorphic rock named. The forces creating reverse faults are compressional pushing the sides together.
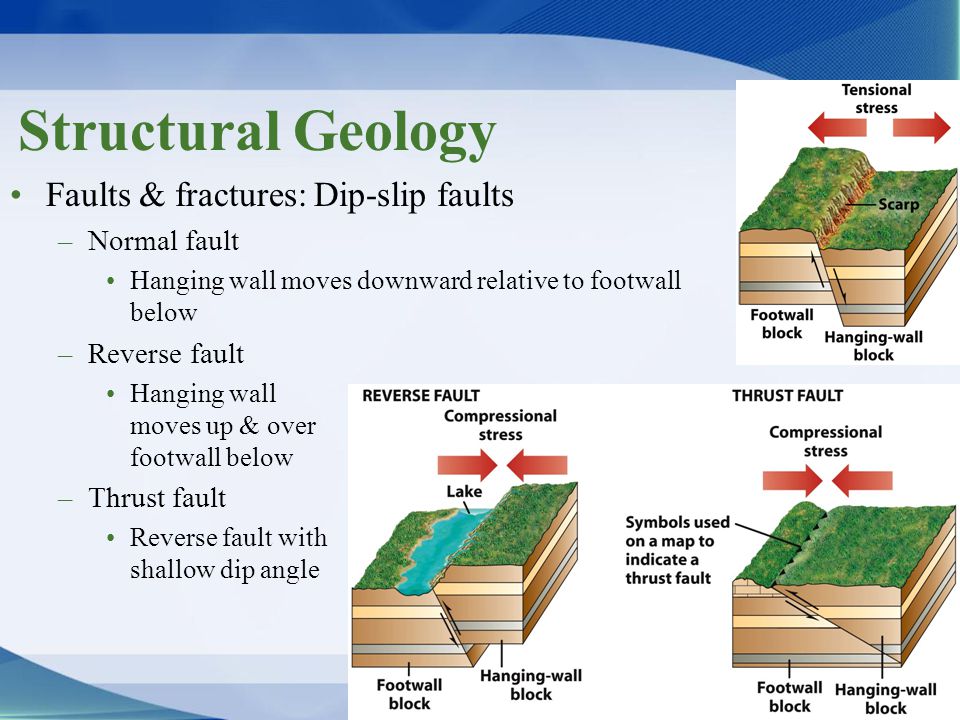
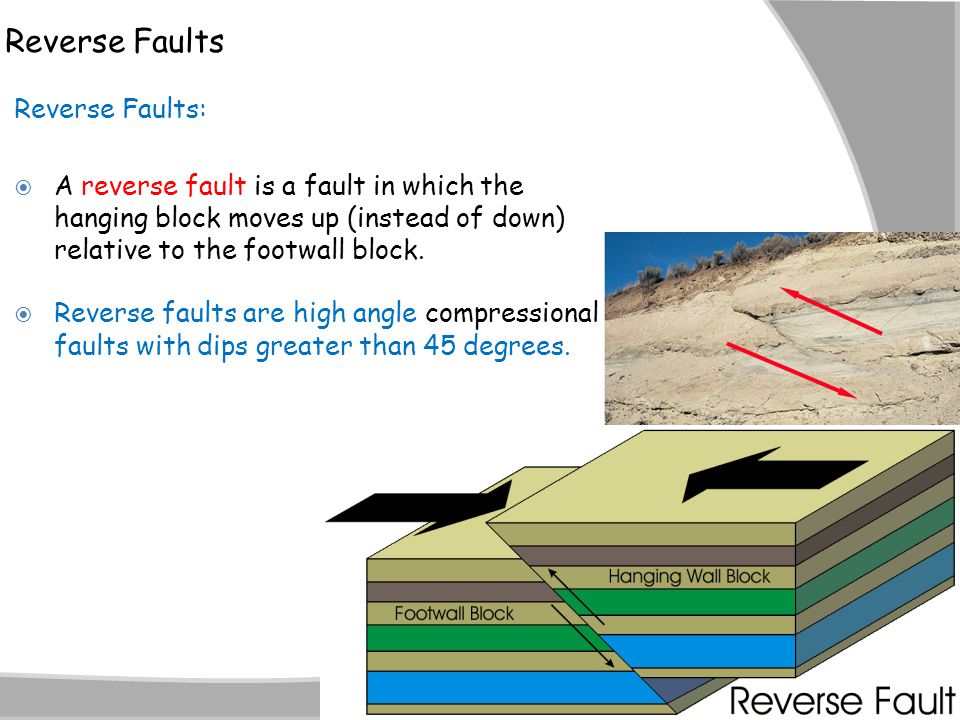
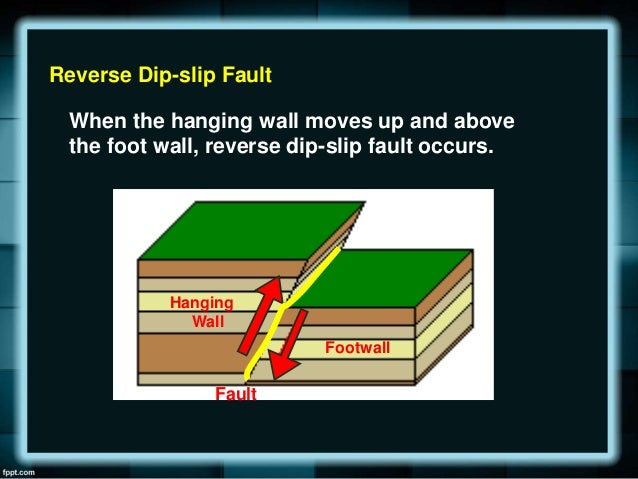
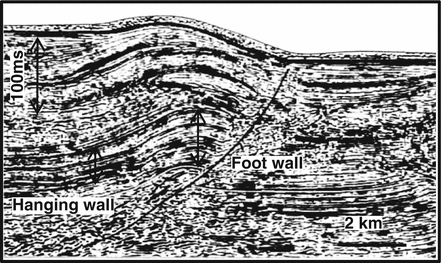
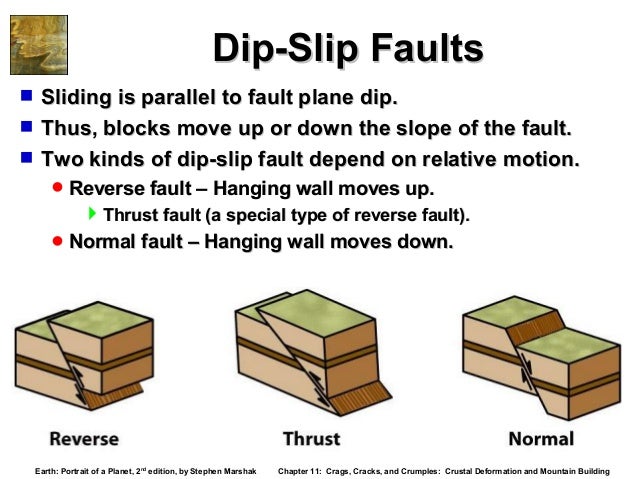
The hanging wall occurs above the fault plane and the footwall occurs below it. The fault plane is greater than 35 from horizontal and the hanging wall block moves upward relative to the footwall block shear stress at sufficient depth within a fault plane can induce ductile shear forming a fine grained metamorphic rock named. The hanging wall moves up and over the footwall. Basin and range region.
During an earthquake if a footwall slides upward relative to a hanging wall as shown in the figure below the fault is termed a fault. They are common at convergent boundaries. Edges of horsts and grabens. With compressional forces the hanging wall moves upward relative to the footwall.
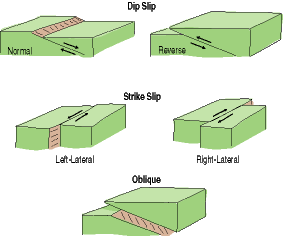
Zones of crustal extension. Thrust faults are reverse faults that dip less than 45. Footwall lies to the left of the hanging wall 55. This terminology comes from mining.
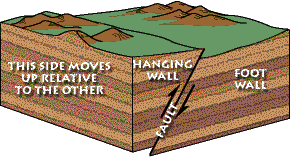
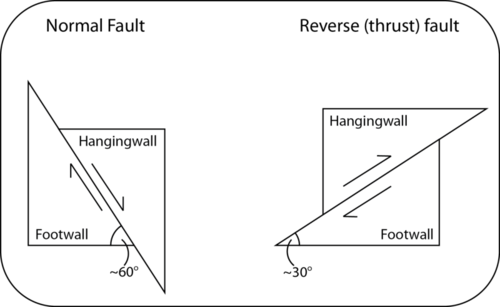
In a fault the fault plane is less than 35 from horizontal and the hanging wall block moves upward relative to the footwall block. If during an earthquake a hanging wall slides upward relative to a footwall the fault is termed if the fault is shallow much closer to horizontal than vetical. In a fault the fault plane is greater than 35 from horizontal and the hanging wall block moves upward relative to the footwall block. Hanging wall and footwall.
The two sides of a non vertical fault are known as the hanging wall and footwall. Together normal and reverse faults are called dip slip faults because the movement on them occurs along the dip direction either down or up respectively. Hanging wall down footwall up. Hanging wall lies vertically above the footwall b.
Hanging wall up footwall down. Boundaries of metamorphic core complexes. This type of fault is referred to as what. Low angle normal fault footwall gneiss hanging wall shallow crust rocks.