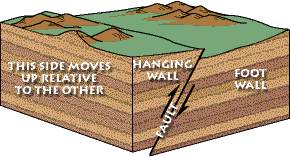
Hanging Wall Moves Down Relative To Football

The hanging wall slides down relative to the footwall.
Hanging wall moves down relative to football. A downthrown block between two normal faults dipping towards each other is a graben. Formed by tensional stress rocks are stretched away from each other. When the hanging wall moves up in relative to the footwall it is called a fault. Low angle normal faults with regional tectonic significance may be designated detachment faults.
Normal faults are common. Dip either east or west. Occurs when the hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall. If a bed strikes north it must.
Rift valleys are formed by the sliding of the hanging walls downward many thousands of metres where they then become the valley floors. When the hanging wall moves down in relative to the footwall it is called a fault. The layer of earths that has the most mass. Normal faults usually form where tectonic plate motions cause tension.
Occurs when opposing when the hanging forces cause rock to break and move horizonally. They bound many of the mountain ranges of the world and many of the rift valleys found along spreading margins of tectonic plates. A map symbol similar to the letter t is used to record on a map. A dip slip fault in which the block above the fault has moved downward relative to the block below.
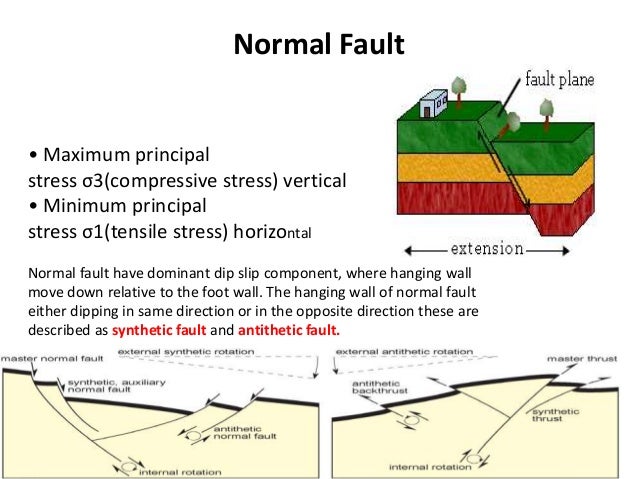
The hanging wall moves down relative to the foot wall. These usually occur when tectonic forces cause tension that pulls rocks apart. Tension is stress that pulls rocks apart. The theory that continents move apart from each other.
A n fault forms when the hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall. Occurs when the hanging wall moves down relative to the foot wall reverse fault. In a normal fault the hanging wall moves downward relative to the footwall. An upthrown block between two normal faults dipping away from each other is a horst.
This type of faulting occurs in response to extension. A dip slip fault in which the upper block above the fault plane moves up and over the.