Hanging Ends Of Alveolar Walls Emphysema Histology
It is one end of the spectrum of copd resulting from the smoking of tobacco.
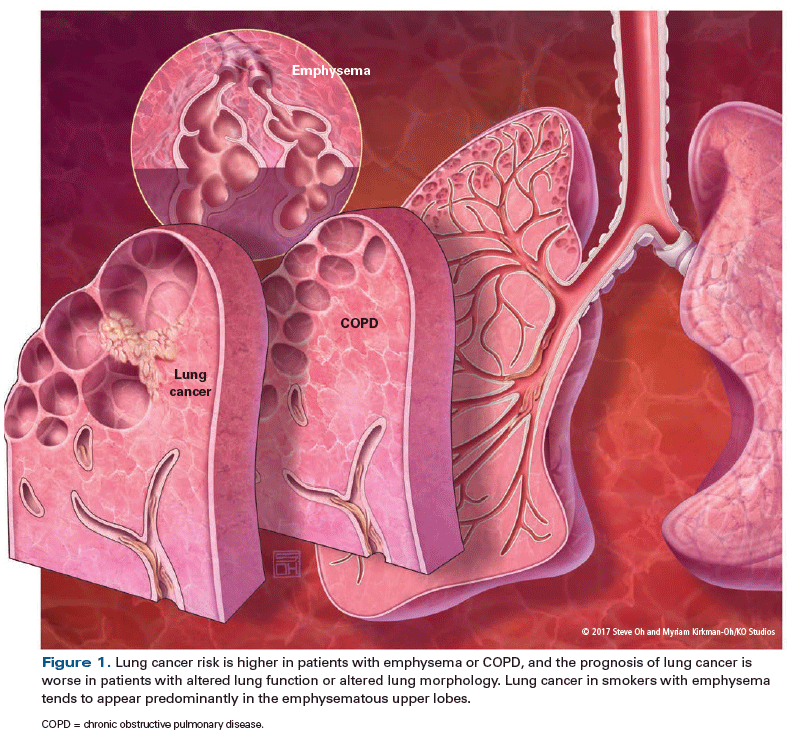
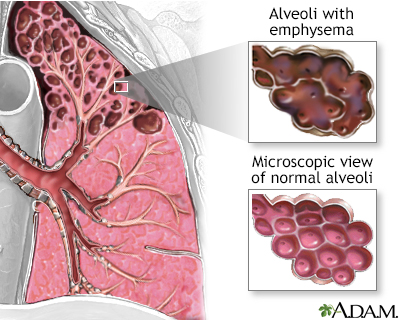
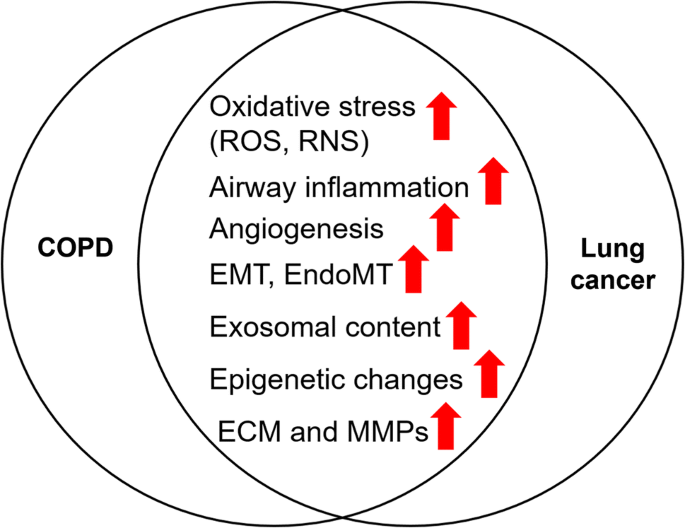
Hanging ends of alveolar walls emphysema histology. Pulmonary emphysema is defined as the abnormal permanent enlargement of the airspaces distal to the terminal bronchioles accompanied by destruction of the alveolar wall and without obvious fibrosis. A chest ct scan of a 56 year old man with copd demonstrating a profound loss of the lung parenchyma and paucity of lung vessels b whole lung section demonstrating ubiquitous holes i e emphysema c histology of end stage emphysematous lung h e staining. Type 1 squamous alveolar epithelial cells. Emphysema is one of the entities grouped as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease emphysema is best evaluated on ct although indirect signs can be noticed on conventional radiography in a.
Senile emphysema due to age related alteration of acini. Chronic lower respiratory disease primarily copd is the third leading cause of death in the united states and the fourth leading cause of death worldwide although it may become the fourth global cause of death in 2020. 2014 12 3 382 3 distal air spaces of terminal bronchiole 2 in addition evidences of destruction of alveolar wall and fibrosis. Histopatological caracteristics of pulmonary emphysema 383 einstein.
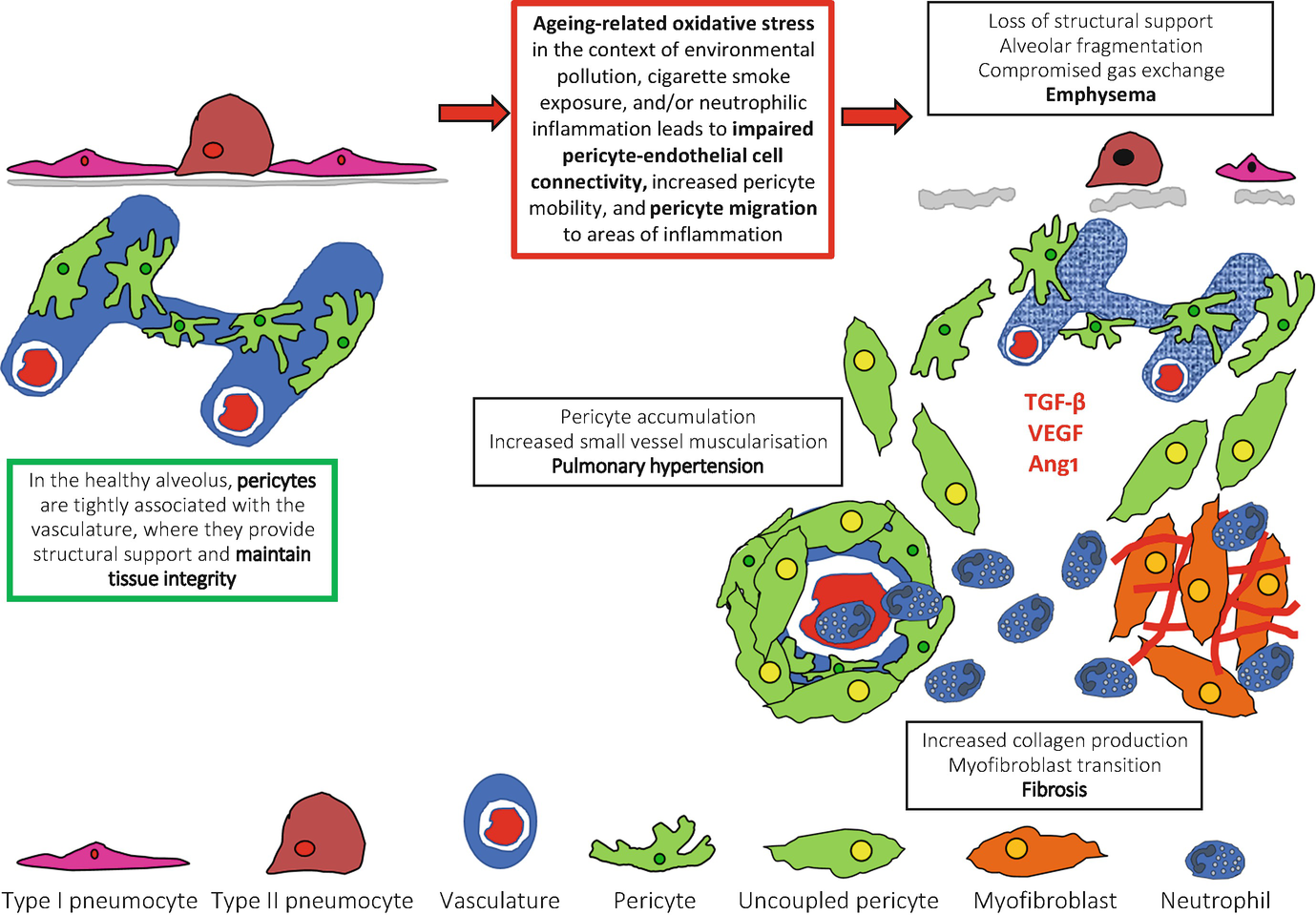
Constituting 95 of the alveolar surface area 8 the type 1 cells are extremely thin and flexible to help in the process of gas diffusion so the oxygen carbon dioxide exchange can occur between the alveoli and the. Pulmonary emphysema defines permanent dilatation of airspaces due to destruction of alveolar walls. The loss of alveolar septal cells is not accompanied in this specimen by significant. Emphysema in the emphysemateous lung air spaces become enlarged due to increased compliance and destruction of the alveolar walls.
The one cell thick walls of the alveoli are composed of two distal airway epithelium cell types pneumocytes 7. Bullous emphysema formation of multiple bullae 1 cm with thin wall can cause bullae inflation and pneumothorax. Emphysema can be defined as having a loss of lung elasticity permanent enlargement of the air spaces distal to the terminal bronchioles and destruction of the alveolar walls. It can be classified under the umbrella term chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder copd 1.
Almost 15 7 million americans 6 4 in 2014 reported that they were diagnosed with copd however the actual number is likely much higer. Congenital lobar emphysema pediatr clin north am 1994 41 453 hyperinflation of one or more lobes due to malformation of. There are three types of emphysema. Pulmonary emphysema is caused by enzymatic imbalance between proteases and anti proteases that results in destruction of the alveolar wall due to proteolytic enzymes action which affects the extracellular matrix ecm and its component integrity especially the elastic fibres.